What is it?
Biodynamic agriculture is a system of agricultural production that seeks to harmoniously integrate the ecological, economic and social aspects of farming. Developed in the 1920s by Austrian philosopher and scientist Rudolf Steiner, biodynamic agriculture is based on principles that go beyond the merely organic, incorporating a spiritual and holistic view of the natural world. This approach focuses not only on food production, but also on the health of soil, plants, animals and humans, considering the farm as a living and self-sufficient organism.
History
Biodynamic agriculture has its roots in the lectures given by Rudolf Steiner in 1924, known as the “Agricultural Course”. Steiner, the founder of anthroposophy, proposed that agriculture should be seen as an integral system, where all elements are interconnected and must work in harmony. His teachings are based on the idea that the Earth is a living being and that cosmic and terrestrial forces influence plant growth and soil health.
Steiner introduced concepts such as the importance of lunar and planetary rhythms in agriculture, the use of biodynamic preparations to strengthen soil and plants, and the idea that the farm should be a self-contained and diversified organism. These principles have been developed and applied by farmers and scientists around the world, giving rise to a global movement seeking more sustainable and environmentally friendly agriculture.
Fundamental principles of Biodynamic Agriculture
1. The Farm as a Living Organism
In biodynamic agriculture, the farm is considered a living, self-sufficient organism. This means that there must be a balance between the different components of the farm, such as crops, animals, soil and humans. Diversity is key, as it promotes resilience and reduces dependence on external inputs.
2. Biodynamic Preparations
Biodynamic preparations are natural substances used to strengthen soil and plants. These preparations are made from materials such as manure, quartz and medicinal plants, and are applied in homeopathic quantities. The best known are “Preparation 500” (fermented cow manure in buried horns) and “Preparation 501” (ground quartz in buried horns). These preparations are used to stimulate the biological activity of the soil and improve the quality of crops.
3. Cosmic and Terrestrial Rhythms
Biodynamic agriculture takes into account cosmic and terrestrial rhythms, such as lunar phases and planetary cycles, when planning agricultural activities. These rhythms are believed to influence plant growth and soil health. For example, planting and harvesting during certain lunar phases is recommended for best results.
4. Crop Rotation and Plant Associations
Crop rotation and plant companionship are fundamental practices in biodynamic agriculture. These techniques help maintain soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote biodiversity. Crop diversity also contributes to the health of the agricultural ecosystem.
5. Animal Integration
Animals play an important role in biodynamic agriculture, contributing to nutrient cycling and soil health. Animal manure is used to make compost and biodynamic preparations, which helps maintain soil fertility. In addition, animals are allowed to graze on the fields, which contributes to soil regeneration and weed control.
6. Biodynamic composting
Composting is an essential practice in biodynamic agriculture. Compost is made from organic materials such as manure, crop residues and other plant waste. Biodynamic preparations are added to compost to improve its quality and stimulate microbial activity. Biodynamic compost is used to enrich the soil and promote healthy plant growth.
Benefits of Biodynamic Agriculture
1.Improved Soil Health
Biodynamic agriculture focuses on soil health as a basis for food production. Biodynamic preparations and composting practices help to increase the biological activity of the soil, improve its structure, and increase its capacity to retain water and nutrients. Healthy soil is essential for the growth of healthy plants and the production of nutritious food.
2. Zero-waste foods with great economic value
Food produced through biodynamic agriculture often has a higher nutrient content and better taste compared to conventionally produced food. This is because biodynamic practices promote soil and plant health, resulting in more nutritious and tasty food, as well as zero chemical residues.
3. Environmental Sustainability
Biodynamic agriculture is a sustainable production system that seeks to minimize environmental impact. By promoting biodiversity, reducing the use of external inputs and improving soil health, biodynamic agriculture contributes to the conservation of natural resources and the mitigation of climate change.
4. Resilience to Climate Change
Crop diversity and soil health are key factors that contribute to the resilience of biodynamic farms to the effects of climate change. Healthy soil rich in organic matter is more resistant to drought and flooding, while crop diversity reduces the risk of losses due to pests or diseases.
5. Animal Welfare
In biodynamic farming, animals are treated with respect and provided with a natural and healthy environment. Animals have access to pasture and are fed with feed produced on the farm, which contributes to their well-being and the quality of animal products such as milk and meat.
Challenges and challenges in Biodynamic agriculture
Despite its many benefits, biodynamic agriculture also faces challenges and issues that hinder its expansion.
1. Complexity and Knowledge Requirements
Biodynamic agriculture requires a high level of knowledge and skills from farmers. The preparation and application of biodynamic preparations, as well as the planning of agricultural activities according to cosmic rhythms, can be complex and require specialized training.
2. Certification and Market
Although there is a biodynamic certification (Demeter), the market for biodynamic products is still limited compared to conventional organic products. This can represent a challenge for farmers who want to adopt this production system, as they may face difficulties in marketing their products.
Esseeds and Biodynamic agriculture
Thanks to the Crescent Sunn seed (Crotalaria juncea – Sunn hemp), Esseeds has been working in biodynamic agriculture for years, thanks to the benefits it has for improving soil, both physically and chemically, and its ability to attract auxiliary fauna and pollinators.
In an agricultural system where sustainability and the diversity of flora and fauna are prioritized, Crescent Sunn is essential due to its short crop cycle period (7 weeks) and the minimal absorption of natural resources from the agricultural soil that it uses for its development.
The purpose
Biodynamic agriculture represents a holistic and sustainable approach to food production, which seeks to integrate the ecological, economic and social aspects of agriculture. Through practices such as the use of biodynamic preparations, consideration of cosmic rhythms and the promotion of biodiversity, biodynamic agriculture offers a viable alternative to conventional agricultural systems.
Biodynamic agriculture has proven to be an effective system for improving soil health, producing high-quality food, and promoting environmental sustainability. As more farmers and consumers become interested in more environmentally friendly production methods, biodynamic agriculture has the potential to play an important role in the transition to a more sustainable food system.
In a world facing challenges such as climate change, soil degradation and biodiversity loss, biodynamic agriculture offers a vision of how we can work in harmony with nature to produce healthy food using natural products to control and manage production.
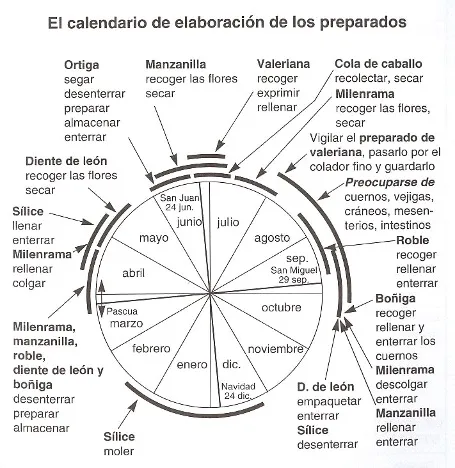
Finally, we share the agricultural calendar from the www. Biodynamic.es page where the researcher Maria Thun presents a postscript on the relationship between the constellations and Organic – Dynamic agriculture.
AGRICULTURAL CALENDAR
Cosmic forces
The Earth is embedded in our solar system and planetary forces leave their mark on the morphology of plants. Biodynamic farmers use this knowledge to choose the right dates for sowing, tilling, treatment and harvesting, in practice, according to the cosmic forces active at the time (as far as climatic conditions allow).
These cosmic effects have been investigated by Hartmut Spiess (of the German Institute for Biodynamic Research) and, among many others, by Maria Thun:
…with regard to sowing and cultivation work, let us remember that every time the soil is worked, cosmic forces are introduced into it and can positively or negatively influence the results of these actions.

«In every living organism, formative forces act: physical, etheric, astral and spiritual.
In plants, physical and etheric forces act from within.
the astral forces around her and the spiritual forces from vast, distant stellar reaches.»
— Rudolf Steiner founder of Biodynamic Agriculture