Crescent Sunn
Use of green manure
- Water and wind erosion control
- Weed control
- Increased soil macro and micro porosity
- Control of fungal soil attacks
- Population control of different types of nematode family
- Large fixation of U.F. of Nitrogen, in addition to P and K
- Incorporation of fast mineralizing organic matter
- Increase in auxiliary fauna
Forage use
- Short cycle (ideal as a second crop)
- Outstanding percentage of proteins
- High percentage of energy
- Use for both hay and silo
- High palatability
- High in vitro digestibility
- Making a forage use also performs soil improvement
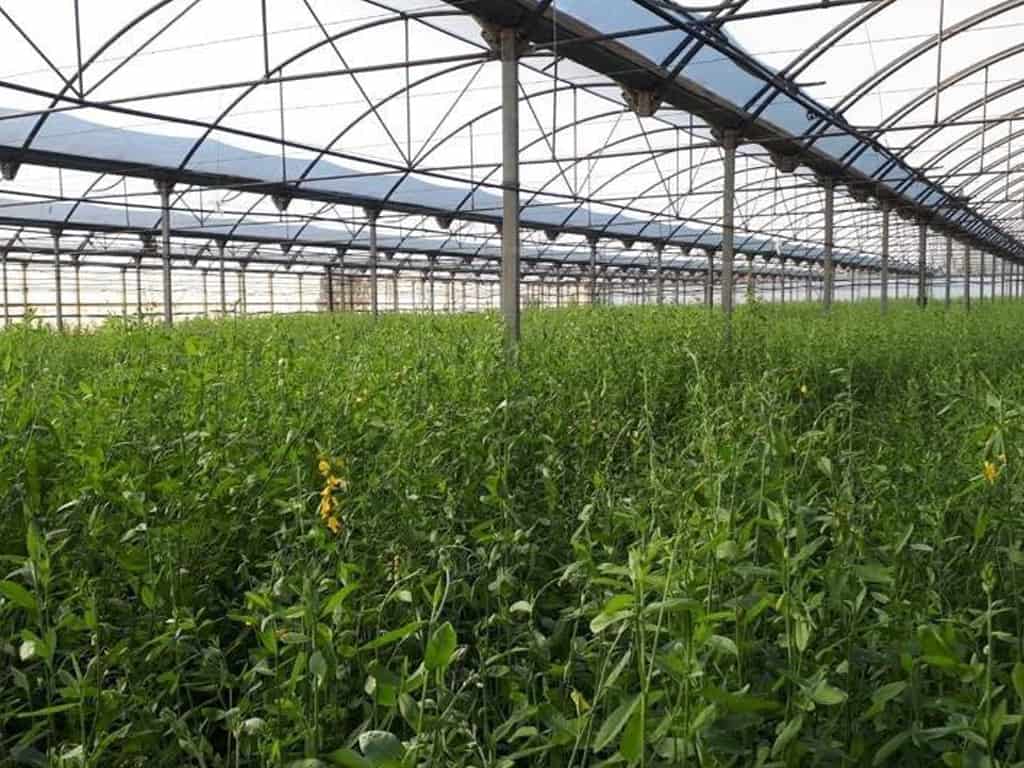
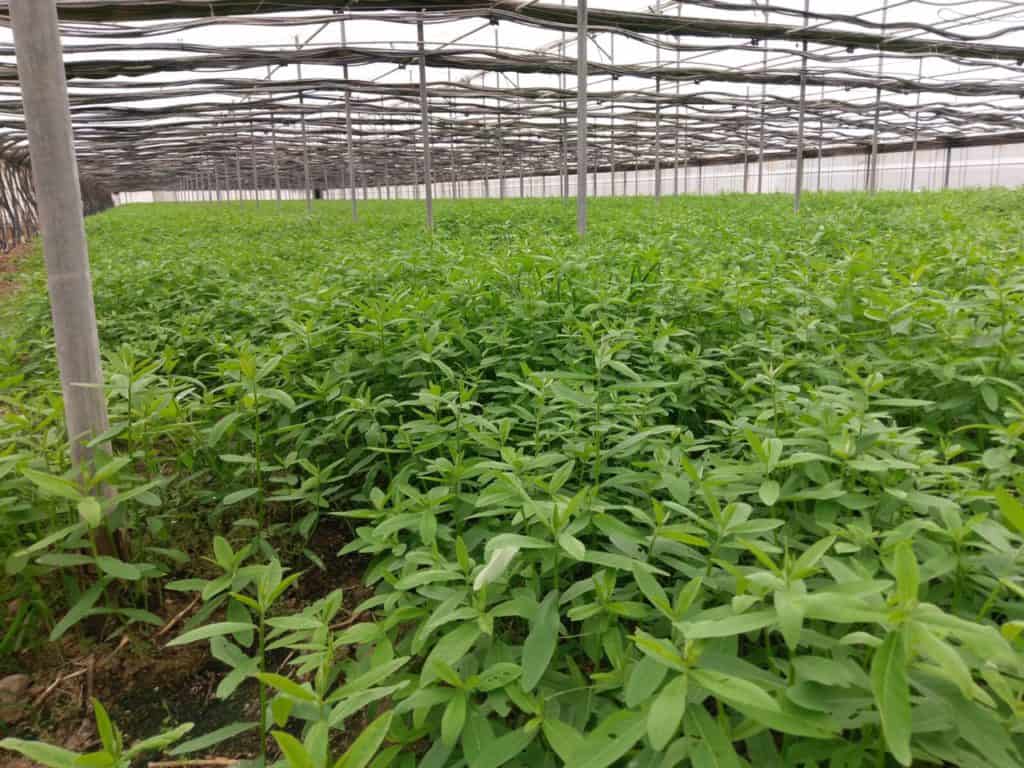
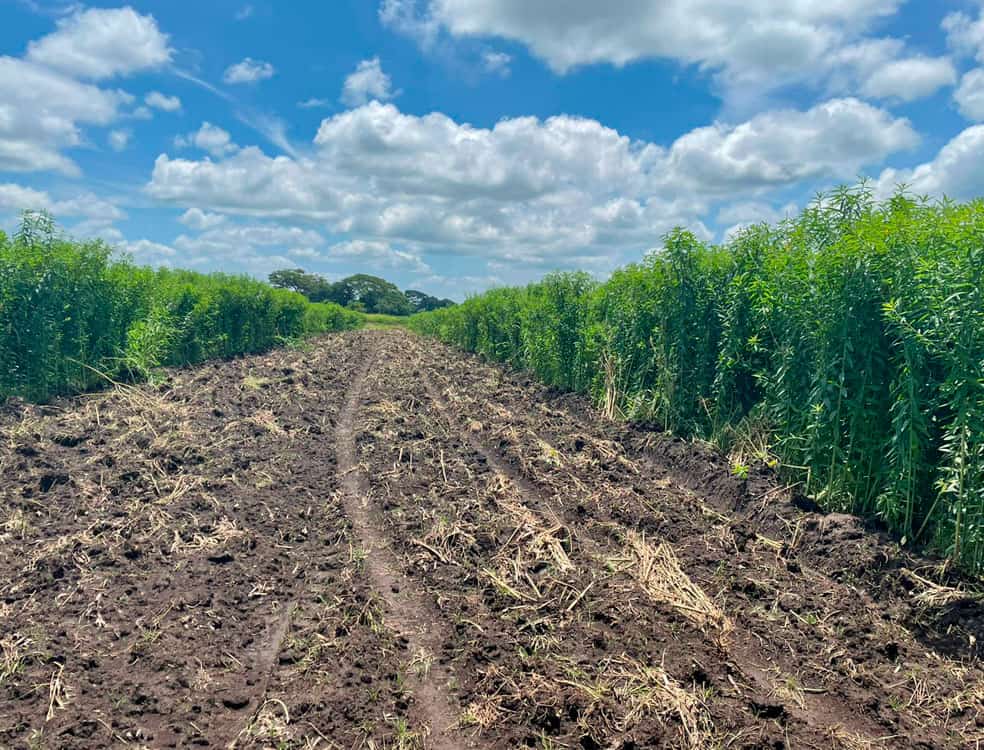
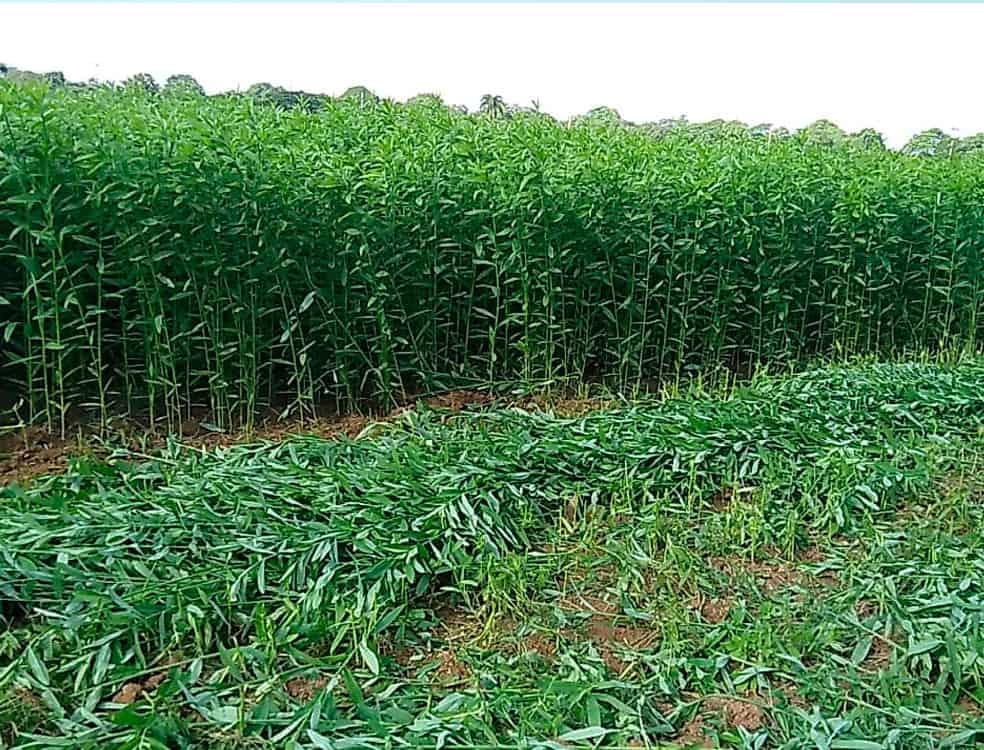




Sheet
Scientific name of the species
Crotalaria juncea
Common name of the species
Crescent Sunn
Vegetative cycle
Annual, 6 to 8 weeks
Growth
Erect
Height
1.2 - 1.8 m
Growing season
Warm season
Diffusion
Seeds
Soils
Deep, well drained. Sandy, silty and loamy loam
Drought tolerance
Loud
Frost tolerance
Casualty
Salinity tolerance
Medium - high
Flood tolerance
Does not tolerate
Total dry matter production/ ha
5,000 - 7,000 kg of dry matter / ha
Palatability
Excellent
Toxicity
No
Planting period
From the beginning of the hot season
Planting density
30 - 40 kg / ha
Planting depth
1-2 cm
Remarks
Use as cover crops and forage production
Implementation of Crescent Sunn
Preparation of the land
Sowing and establishment
- The use of compactor curl in sandy soils improves the quality of planting based on the uniform acceleration of seed germination (not recommended for clay soils).
- It can be sown in direct sowing obtaining excellent results.
Irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation:
- Germination irrigation, of the amount necessary to make the moisture in the soil homogeneous, taking into account the climatic factors (wind, the type and texture of the soil, orography of the terrain). Fournir suffisamment d’eau pour rassembler l’humidité dans le sol, en utilisant un volume d’eau élevé pour éviter les problèmes de “cuisson” de la graine dus aux températures élevées à la date de plantation, en évitant toujours l’engorgement.
- Subsequent irrigations: taking into account the climatic factors (wind, the type and texture of the soil, orography of the terrain) must be carried out at the request of the plant, the symptoms of irrigation needs are flaccidity and decay of the leaves.
- The water needs of the plant are increasing according to the growth of the plant, having to provide more water as the plant grows.
- In a first stage (still small plant) the plant does not tolerate an excess of water correctly.
Irrigation on foot or flooding
- First irrigation germination, with this type of irrigation takes even more importance the use of the roller compactor to avoid the possible dragging of the seed (provided that the texture of the soil allows us).
- Second half-cycle irrigation: it should be provided when the crop is in the middle of the cycle. However, as we indicated in sprinkler we must analyze the water need of the plant, being able to advance or delay irrigation at the request of the crop.
Management use of green or fodder fertilizer
Green manure
It must be incorporated into the soil during week 7 or 8 from planting, for the incorporation of organic matter not excessively fibrous and thus achieve its rapid mineralization. It is advisable to use it together with the inoculant seed to enhance its nitrogen fixation action.
Forage
Weed control
Crescent Sunn is one of the Fabaceae families which implies that it is classified as a broadleaf crop.
Narrow leaf weed control: Narrow leaf weed control can be done in pre-sowing or post-planting using any selective herbicide we find on the market.
Control of broadleaf weeds: this crop is a broadleaf crop we must take many precautions when choosing the herbicide to combat broadleaf. Exclusively as a tested herbicide we can recommend in pre-emergency Pendimetaline 45.5% at a dose of 2 liters hectare. The correct application must be carried out with the seed established in the soil and after its application perform an irrigation for its perfect action.
Fertilization
Diseases
Videos
Contact us
- Responsible: Efecto Soluciones S.L.
- Purpose of the collection and processing of personal data: to manage the request you make in this contact form.
- Rights: You can exercise your rights of access, rectification, limitation and deletion of the data in info@efectosoluciones.com, as well as the right to file a claim with a control authority.
- Additional information: In the privacy policy you will find additional information about the collection and use of your personal information. Including information on access, preservation, rectification, deletion, security and other topics.
