What is a tetrazolium analysis for agricultural seeds?
Tetrazolium analysis is a widely used technique in agriculture to assess seed viability. This method is rapid, accurate, and allows for determining whether a seed is alive and has the potential to germinate, even without having to wait the time required for a traditional germination test. It is especially useful for farmers, seed producers, and quality control laboratories seeking to ensure the quality of their seed batches.
What is tetrazolium analysis?
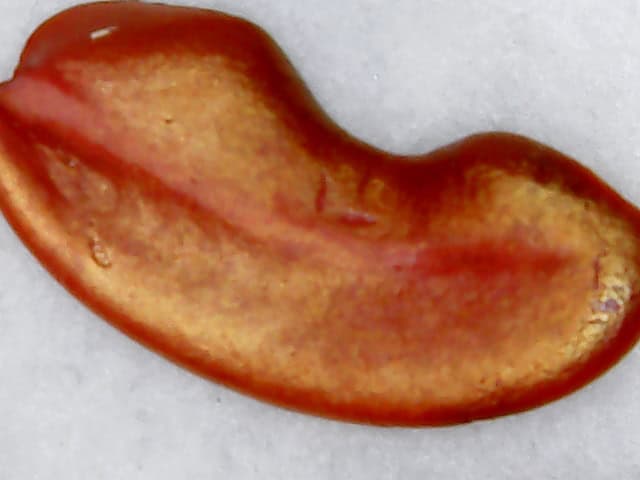
Tetrazolium analysis is based on the ability of living seed cells to perform metabolic processes. When a seed is alive, its metabolically active tissues reduce a chemical compound called 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (or simply tetrazolium) to a red-colored compound called formazan. This color change indicates that the cells are alive and functioning.
The procedure involves the following basic steps:
1. Seed preparation: Seeds are hydrated to activate their metabolism. This may include soaking them in water or subjecting them to controlled humidity conditions.
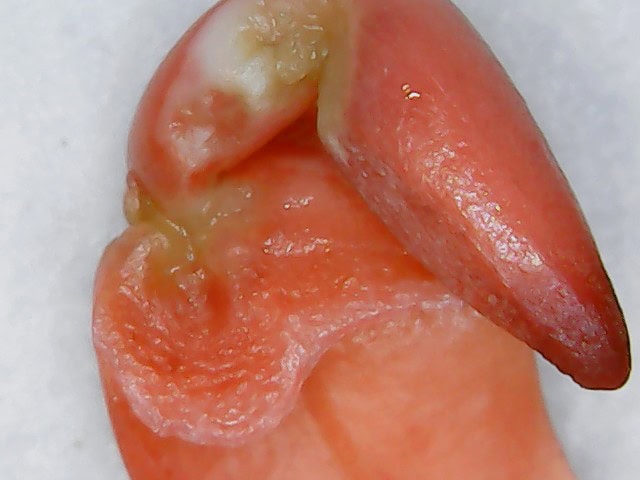
2. Cutting or scarification: A cut or opening is made in the seed to expose the internal tissues, allowing the tetrazolium to penetrate the metabolically active areas.
3. Immersion in tetrazolium solution: Seeds are immersed in a tetrazolium solution, usually at a concentration of 0.1% to 1%, and incubated at a specific temperature (usually between 30 and 40 °C) for a specified period of time.
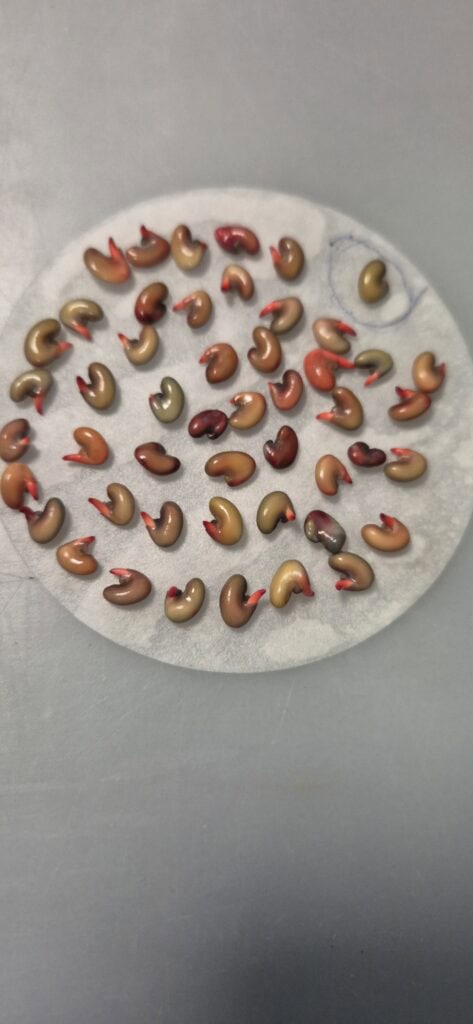
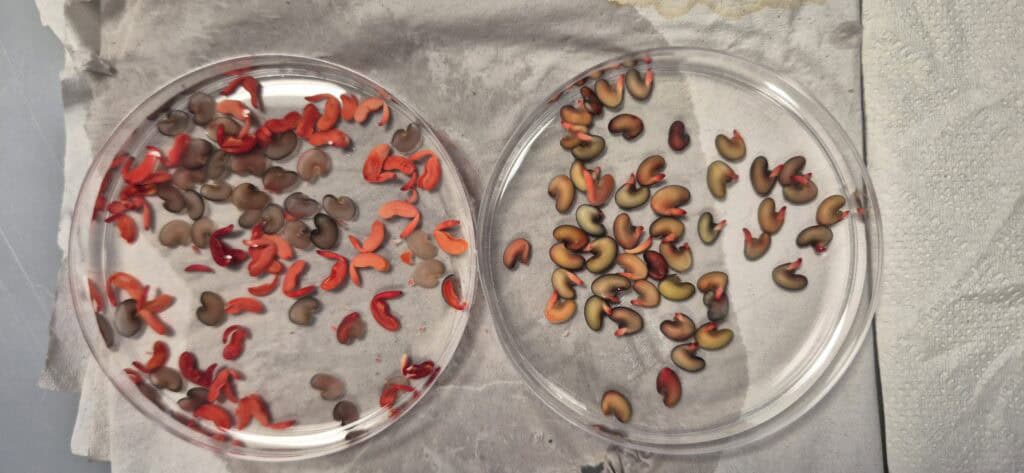
4. Visual evaluation: After incubation, the seeds are examined under a magnifying glass or microscope. Living tissue stains red, while dead tissue remains colorless or pale.
What information does the analysis provide?
Tetrazolium analysis not only determines whether a seed is alive, but can also identify specific problems within seed tissues, such as mechanical damage, deterioration due to aging, or damage caused by pests or diseases. This makes it a valuable tool for:
– Evaluate the quality of a seed batch before sowing.
– Diagnose germination problems in stored seeds.
– Determine the viability of seeds of species with long dormancy periods.
Advantages of tetrazolium analysis
– Speed: Results are obtained in a matter of hours, compared to the days or weeks that a germination test can take.
– Accuracy: Allows you to identify viable seeds even if they would not germinate under normal conditions due to dormancy.
– Versatility: It is applicable to a wide variety of agricultural species, from grasses such as Siambasa Grass to legumes such as alfalfa or Crescent Sunn.
Limitations of the analysis
Although it is a very useful technique, tetrazolium analysis requires trained personnel to interpret the results correctly. Furthermore, it does not directly measure germination capacity, but rather viability, so it must be complemented with other tests in some cases.
Tetrazolium analysis is an essential tool for those working with agricultural seeds, allowing them to quickly assess the viability of a seed lot and make informed decisions about its use. For seed producers and marketers, such as those working with species like Crescent Sunn, alfalfa, or hairy vetch, this analysis can make the difference between a successful crop and one with germination problems. Implementing this technique in quality control processes ensures high-quality seeds and, ultimately, improved agricultural yields.